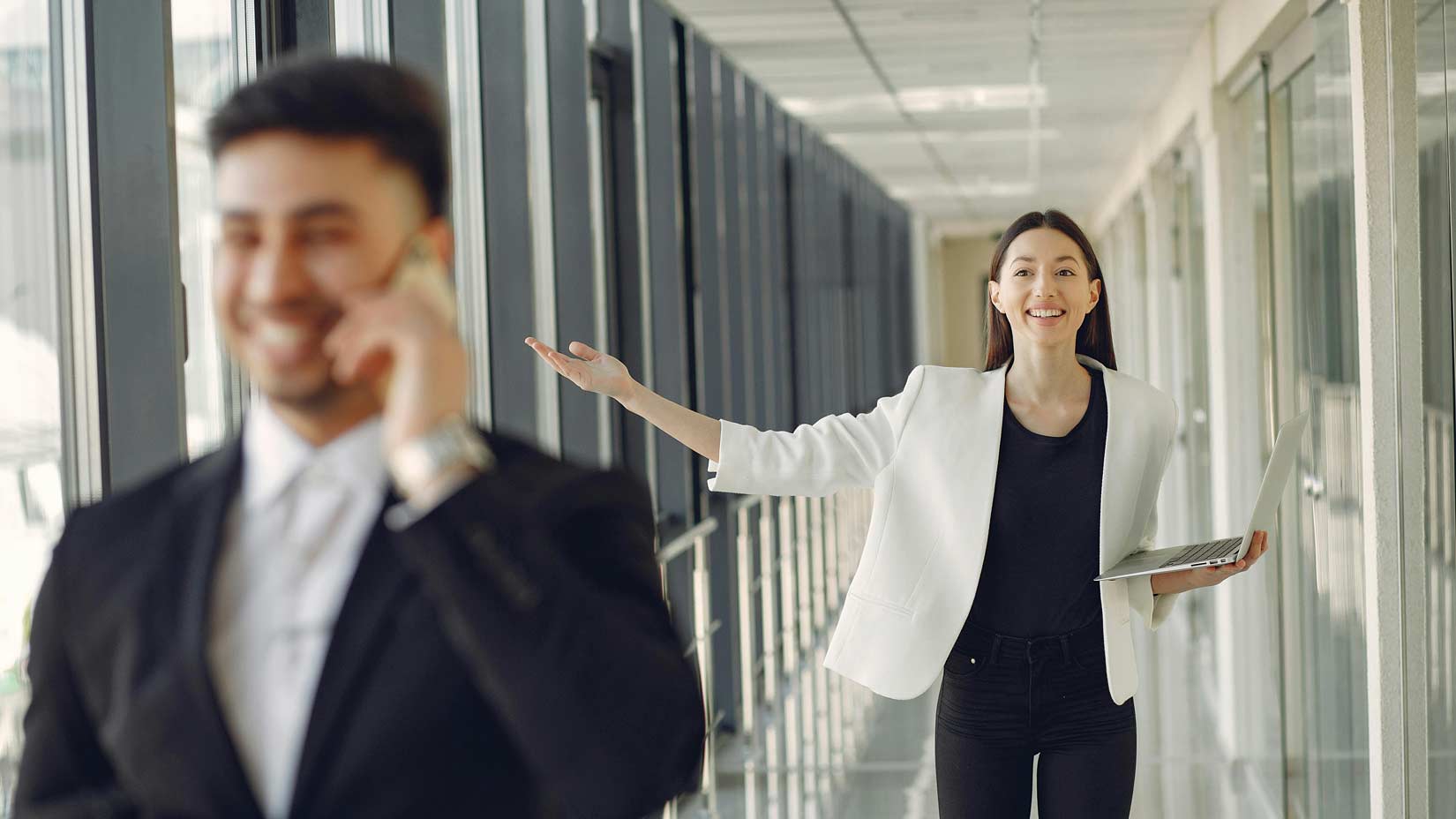
A recent study, reported by The Guardian, sheds light on how these AI related technological advancements could reshape the traditional work model to a 4 days working week.
Legal Initiative started in the USA
In the United States, Congressman Mark Takano has introduced a bill proposing a 32-hour workweek. His rationale is deeply rooted in the evolving landscape of the workforce due to AI and automation. “Fundamental changes are coming to our workforce,” Takano stated, emphasizing the need for government measures to ensure that the efficiency gains from these technologies benefit all workers, regardless of their industry or skill level.
The Impact of AI on Productivity and Work-Life Balance
The study, focusing on companies in the UK and the USA that have already integrated AI into their economic and commercial processes, brings interesting findings. Autonomy, a think-tank specializing in economic research, noted a productivity increase and an improvement in the work-life balance for 28% of employees – amounting to 8.8 million people in the UK and 35 million in the USA. While these results are not yet groundbreaking, projections suggest that by 2033, companies could reduce the weekly hours of an employee from the current 40 hours to 32 hours without sacrificing performance or cutting wages. This could lead to either a four-day workweek or a reduction in daily working hours.
Implications and Future Prospects
This shift could have profound implications for the workforce. A shorter workweek could lead to improved mental health, more time for personal pursuits, and a better balance between work and life. It also presents challenges, such as the need for re-skilling and adapting to new work environments.
The intersection of AI, automation, and the labor market is paving the way for significant changes. The 32-hour workweek might soon become a reality, symbolizing a pivotal shift in how we perceive and engage with work in the 21st century.