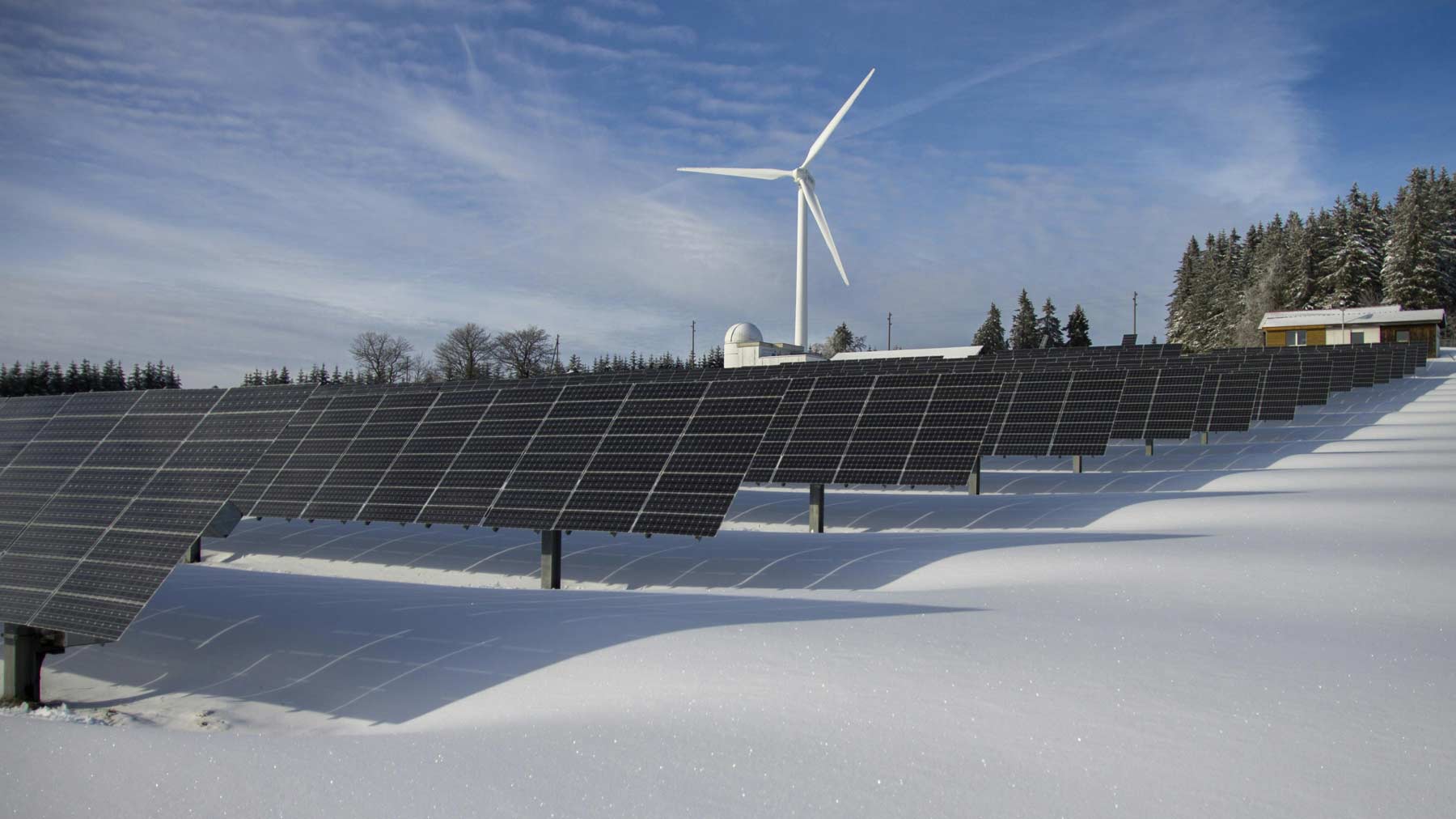
A recent report the International Energy Agency (IEA) predicts a significant shift in global energy production trends. By next year, renewable energy sources are expected to provide more than one-third of global electricity, surpassing coal as the primary energy source. This marks a pivotal moment in the global energy landscape.
Increasing Demand for Electricity
The report highlights an accelerated global demand for electricity in the coming years. Despite this rise, the production of renewable energy is anticipated to be sufficient to meet the growing needs. After a slight decline in global electricity demand by 2.2% in 2023, mainly due to reduced needs in advanced economies, experts now expect an increase of up to 3.4% between 2024 and 2026. Approximately 85% of this demand is projected to come from outside advanced economies, particularly China, India, and other Southeast Asian countries.
The Rise of Renewable and Nuclear Energy
In response to the increasing global energy demand, renewable sources like solar, wind, hydroelectric, and nuclear energy are expected to play a crucial role in reducing the reliance on fossil fuels. By 2026, renewable energy is estimated to account for nearly half of the world’s electricity production, overtaking coal as the main source for households.
Moreover, nuclear energy production is projected to reach an all-time high globally by 2025. This surge is attributed to increased production in France, the reactivation of several plants in Japan, and the commencement of commercial operations of new reactors in China, India, Korea, and Europe. Experts note that when the use of fossil fuels falls below 60% globally, it will mark a historic threshold set by the IEA over 50 years ago.
Impact on Environmental Goals
The shift towards less polluting and renewable technologies significantly impacts the environment. The report indicates that electricity accounted for 20% of the final energy consumption in 2023, up from 18% in 2015. However, experts caution that meeting the world’s climate objectives will require a much more rapid advancement in electrification in the coming years.
This transition to renewable energy sources not only addresses the increasing global demand for electricity but also aligns with the urgent need to combat climate change and reduce environmental pollution.